What is the production process for mainstream capacitor specifications?
What is the Production Process for Mainstream Capacitor Specifications?
I. Introduction
Capacitors are fundamental components in electronic devices, serving as energy storage elements that play a crucial role in various applications, from power supply circuits to signal processing. They store electrical energy temporarily and release it when needed, making them essential for maintaining stable voltage levels and filtering signals. As technology advances, the demand for capacitors with specific characteristics has increased, leading to the development of various mainstream capacitor specifications. This blog post will explore the production process of capacitors, detailing the types, specifications, manufacturing steps, challenges, and future trends in the industry.
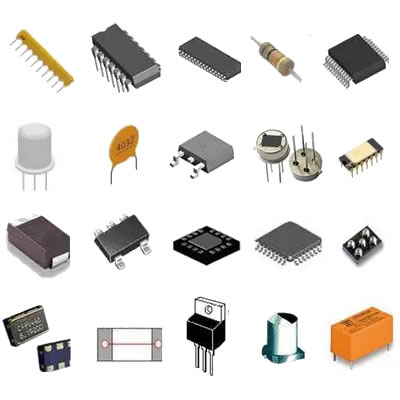
II. Types of Capacitors
Capacitors come in various types, each with unique characteristics and applications. Understanding these types is essential for grasping the production process.
A. Ceramic Capacitors
Ceramic capacitors are widely used due to their small size, low cost, and excellent stability. They are made from ceramic materials and are often used in high-frequency applications. Their characteristics include high capacitance values, low equivalent series resistance (ESR), and a wide temperature range. Common applications include decoupling, filtering, and timing circuits.
B. Electrolytic Capacitors
Electrolytic capacitors are polarized capacitors that offer high capacitance values in a relatively small package. They are made using an electrolyte and are commonly used in power supply circuits, audio equipment, and energy storage applications. Their characteristics include high capacitance, low cost, and a limited voltage range. However, they have a shorter lifespan compared to other types of capacitors.
C. Film Capacitors
Film capacitors are made from thin plastic films and are known for their stability and reliability. They are used in applications requiring high precision, such as audio equipment, power electronics, and timing circuits. Their characteristics include low ESR, high insulation resistance, and a wide temperature range. Film capacitors are often preferred for their long lifespan and low self-heating.
D. Tantalum Capacitors
Tantalum capacitors are known for their high capacitance values and small size. They are made from tantalum metal and are used in applications where space is limited, such as in mobile devices and aerospace electronics. Their characteristics include high reliability, low ESR, and a stable capacitance over a wide temperature range. However, they are more expensive than other types of capacitors.
III. Key Specifications of Capacitors
When discussing capacitors, several key specifications are essential to understand their performance and suitability for specific applications.
A. Capacitance
Capacitance is the primary specification of a capacitor, measured in farads (F). It indicates the amount of electrical charge a capacitor can store. Different applications require different capacitance values, ranging from picofarads (pF) to microfarads (µF) and beyond.
B. Voltage Rating
The voltage rating indicates the maximum voltage a capacitor can handle without breaking down. Exceeding this rating can lead to catastrophic failure. It is crucial to select capacitors with appropriate voltage ratings for specific applications.
C. Tolerance
Tolerance refers to the allowable variation in capacitance from the specified value. It is expressed as a percentage and is critical for applications requiring precise capacitance values.
D. Temperature Coefficient
The temperature coefficient indicates how capacitance changes with temperature. Different materials have different temperature coefficients, affecting the capacitor's performance in varying environmental conditions.
E. Equivalent Series Resistance (ESR)
ESR is a measure of the internal resistance of a capacitor, affecting its efficiency and performance. Lower ESR values are desirable, especially in high-frequency applications.
F. Lifetime and Reliability
The lifetime of a capacitor is influenced by factors such as temperature, voltage, and operating conditions. Reliability is crucial, especially in critical applications, and manufacturers often provide lifetime ratings based on testing.
IV. The Production Process of Capacitors
The production process of capacitors involves several steps, from raw material selection to final testing. Each step is crucial for ensuring the quality and performance of the final product.
A. Raw Material Selection
The first step in capacitor production is selecting the appropriate raw materials. Different types of capacitors require different materials. For example, ceramic capacitors use ceramic powders, while electrolytic capacitors use aluminum or tantalum. Quality control measures are implemented to ensure that the materials meet the required specifications.
B. Manufacturing Steps
1. Dielectric Layer Formation
The dielectric layer is a critical component of capacitors, as it separates the electrodes and stores electrical energy. Various methods are used to form the dielectric layer, including deposition and layering techniques. The dielectric properties of the material significantly impact the capacitor's performance, making this step crucial.
2. Electrode Preparation
Electrode preparation involves selecting the appropriate materials, such as aluminum for electrolytic capacitors or tantalum for tantalum capacitors. Techniques for electrode formation vary, including etching and anodization, which enhance the surface area and improve performance.
3. Assembly Process
The assembly process involves layering and stacking the dielectric and electrode materials to form the capacitor structure. This step may also include encapsulation and sealing to protect the capacitor from environmental factors and ensure reliability.
4. Testing and Quality Assurance
Once assembled, capacitors undergo rigorous testing to ensure they meet the required specifications. Electrical testing checks parameters such as capacitance, voltage rating, and ESR. Environmental testing assesses performance under various conditions, while reliability testing evaluates the capacitor's lifespan and durability.
V. Challenges in Capacitor Production
The production of capacitors is not without its challenges. Manufacturers face several issues that can impact the quality and availability of capacitors.
A. Material Sourcing
Sourcing high-quality materials is essential for capacitor production. Fluctuations in the availability and cost of raw materials can affect production schedules and pricing.
B. Technological Advancements
As technology evolves, manufacturers must keep up with advancements in materials and production techniques. This requires continuous investment in research and development to remain competitive.
C. Environmental Regulations
Manufacturers must comply with environmental regulations regarding material usage and waste disposal. This can add complexity to the production process and increase costs.
D. Market Demand Fluctuations
The demand for capacitors can fluctuate based on market trends and technological advancements. Manufacturers must be agile in their production processes to adapt to changing market conditions.
VI. Future Trends in Capacitor Production
The capacitor industry is evolving, with several trends shaping the future of production.
A. Innovations in Materials
Research into new materials, such as organic and nanomaterials, is ongoing. These innovations aim to improve capacitor performance, reduce size, and enhance sustainability.
B. Miniaturization and High-Density Capacitors
As electronic devices become smaller and more powerful, the demand for miniaturized and high-density capacitors is increasing. Manufacturers are focusing on developing capacitors that can deliver high performance in compact sizes.
C. Sustainable Manufacturing Practices
Sustainability is becoming a priority in capacitor production. Manufacturers are exploring eco-friendly materials and processes to reduce their environmental impact.
D. Impact of Emerging Technologies
Emerging technologies, such as electric vehicles and renewable energy systems, are driving demand for advanced capacitors. Manufacturers must adapt their production processes to meet the specific needs of these applications.
VII. Conclusion
Capacitors are vital components in modern electronic devices, and understanding their production process is essential for appreciating their role in technology. From raw material selection to rigorous testing, each step in the production process contributes to the quality and reliability of capacitors. As the industry faces challenges and embraces future trends, innovations in materials and manufacturing practices will shape the next generation of capacitors, ensuring they continue to meet the demands of an ever-evolving technological landscape.
VIII. References
- Academic journals on capacitor technology and materials science.
- Industry reports detailing market trends and forecasts.
- Manufacturer specifications and guidelines for various types of capacitors.
This comprehensive overview of the production process for mainstream capacitor specifications highlights the complexity and importance of capacitors in the electronics industry, providing insights into their types, specifications, and future developments.