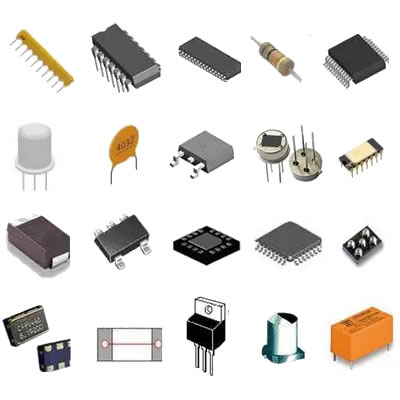
What product types does capacitor factory include?
What Product Types Does a Capacitor Factory Include?
I. Introduction
Capacitors are fundamental components in the world of electronics, serving as energy storage devices that play a crucial role in various applications. They store electrical energy temporarily and release it when needed, making them essential for stabilizing voltage and power flow in circuits. From smartphones to electric vehicles, capacitors are integral to the functionality of countless electronic devices. The capacitor manufacturing industry has evolved significantly over the years, producing a wide range of capacitor types to meet the diverse needs of modern technology. In this blog post, we will explore the various product types included in a capacitor factory, their characteristics, applications, and the manufacturing processes involved.
II. Types of Capacitors
A. Ceramic Capacitors
Ceramic capacitors are among the most widely used capacitors in electronic circuits. They are made from ceramic materials and are known for their small size, high reliability, and excellent temperature stability. Ceramic capacitors are classified into different classes, with Class 1 capacitors offering high stability and low losses, while Class 2 capacitors provide higher capacitance values but with less stability.
**Common Applications:**
Ceramic capacitors are commonly used in decoupling and filtering applications, such as in power supply circuits, audio equipment, and RF circuits. Their small size makes them ideal for compact electronic devices.
B. Electrolytic Capacitors
Electrolytic capacitors are polarized capacitors that use an electrolyte to achieve a larger capacitance value in a smaller package. They are known for their high capacitance and voltage ratings, making them suitable for applications requiring significant energy storage.
**Common Applications:**
These capacitors are often found in power supply circuits, audio amplifiers, and energy storage systems. They are particularly useful in smoothing out voltage fluctuations in power supplies.
C. Film Capacitors
Film capacitors are made from thin plastic films as the dielectric material. They are known for their stability, low self-inductance, and excellent performance in high-frequency applications. Film capacitors can be non-polarized, making them versatile for various applications.
**Common Applications:**
Film capacitors are widely used in audio equipment, power electronics, and timing circuits. Their reliability and performance make them suitable for applications where precision is critical.
D. Tantalum Capacitors
Tantalum capacitors are another type of electrolytic capacitor, but they use tantalum metal as the anode. They are known for their high capacitance-to-volume ratio and stability over a wide temperature range. Tantalum capacitors are also polarized.
**Common Applications:**
These capacitors are commonly used in military and aerospace applications, as well as in portable electronics, due to their reliability and compact size.
E. Supercapacitors
Supercapacitors, also known as ultracapacitors, are energy storage devices that bridge the gap between traditional capacitors and batteries. They can store a large amount of energy and deliver it quickly, making them ideal for applications requiring rapid charge and discharge cycles.
**Common Applications:**
Supercapacitors are used in applications such as regenerative braking systems in electric vehicles, energy storage for renewable energy systems, and backup power supplies.
F. Mica Capacitors
Mica capacitors are known for their high precision and stability. They use mica as the dielectric material, which provides excellent temperature stability and low loss characteristics. Mica capacitors are typically used in high-frequency applications.
**Common Applications:**
These capacitors are often found in RF applications, oscillators, and precision timing circuits, where stability and accuracy are paramount.
G. Aluminum Capacitors
Aluminum capacitors are a type of electrolytic capacitor that uses aluminum oxide as the dielectric. They are known for their high capacitance values and relatively low cost. Aluminum capacitors are polarized and are widely used in various electronic applications.
**Common Applications:**
These capacitors are commonly used in power supply circuits, audio equipment, and consumer electronics due to their affordability and performance.
III. Specialized Capacitors
A. Power Capacitors
Power capacitors are designed to improve the power factor in electrical systems and to provide reactive power support. They are typically used in industrial applications to enhance the efficiency of power systems.
**Common Applications:**
Power capacitors are used in substations, industrial plants, and power distribution systems to reduce energy losses and improve voltage stability.
B. RF Capacitors
RF capacitors are designed for high-frequency applications and are characterized by their low equivalent series resistance (ESR) and low self-inductance. They are essential for maintaining signal integrity in RF circuits.
**Common Applications:**
These capacitors are commonly used in radio transmitters, receivers, and other communication devices where high-frequency performance is critical.
C. High Voltage Capacitors
High voltage capacitors are designed to operate at elevated voltage levels. They are constructed with materials that can withstand high electric fields and are used in applications where voltage spikes are common.
**Common Applications:**
High voltage capacitors are used in power transmission systems, industrial equipment, and medical devices such as defibrillators.
D. Timing Capacitors
Timing capacitors are used in timing circuits to control the timing of events in electronic devices. They are often paired with resistors to create RC timing circuits.
**Common Applications:**
These capacitors are commonly found in clocks, timers, and other applications where precise timing is essential.
IV. Capacitor Components and Accessories
A. Capacitor Banks
Capacitor banks are assemblies of multiple capacitors connected in parallel or series to achieve a desired capacitance value. They are used to improve power factor and voltage stability in electrical systems.
**Description and Purpose:**
Capacitor banks are essential in industrial and commercial applications to reduce energy costs and improve the efficiency of power systems.
B. Capacitor Resistors
Capacitor resistors are used in conjunction with capacitors to control the charging and discharging rates in circuits. They help to manage the time constants in RC circuits.
**Description and Purpose:**
These components are crucial in timing applications and in circuits where precise control of voltage and current is required.
C. Capacitor Connectors
Capacitor connectors are used to connect capacitors to circuits. They come in various forms, including soldered, snap-in, and screw terminals, depending on the application.
**Description and Purpose:**
Proper connectors ensure reliable electrical connections and are essential for the performance and longevity of capacitor-based circuits.
V. Manufacturing Processes
A. Overview of Capacitor Manufacturing
The manufacturing process of capacitors involves several steps, including material selection, component fabrication, assembly, and testing. Each type of capacitor has its unique manufacturing requirements, which can include processes like layering, winding, and encapsulation.
B. Quality Control Measures
Quality control is critical in capacitor manufacturing to ensure reliability and performance. Manufacturers implement rigorous testing protocols, including electrical testing, thermal cycling, and life testing, to ensure that capacitors meet industry standards.
C. Innovations in Capacitor Technology
The capacitor industry is continually evolving, with innovations aimed at improving performance, reducing size, and enhancing energy density. Developments in materials science, such as the use of nanomaterials and advanced dielectrics, are paving the way for next-generation capacitors.
VI. Market Trends and Future Directions
A. Growing Demand for Capacitors in Various Industries
The demand for capacitors is on the rise, driven by the growth of industries such as consumer electronics, automotive, renewable energy, and telecommunications. As technology advances, the need for more efficient and reliable capacitors continues to grow.
B. Technological Advancements
Technological advancements are leading to the development of capacitors with higher energy densities, faster charge and discharge rates, and improved thermal stability. These innovations are essential for meeting the demands of modern electronic applications.
C. Environmental Considerations and Sustainability
As the world becomes more environmentally conscious, capacitor manufacturers are focusing on sustainability. This includes developing eco-friendly materials, reducing waste in the manufacturing process, and creating capacitors that are easier to recycle.
VII. Conclusion
In conclusion, capacitors are vital components in the electronic landscape, with a wide range of types and applications. From ceramic and electrolytic capacitors to specialized types like supercapacitors and RF capacitors, the diversity of products offered by capacitor factories is impressive. As the industry continues to evolve, innovations in manufacturing processes and materials will drive the development of more efficient and sustainable capacitors. The future of the capacitor manufacturing industry looks promising, with growing demand and technological advancements paving the way for new possibilities in energy storage and electronic performance. Understanding the various product types and their applications is essential for anyone involved in electronics, as capacitors will continue to play a crucial role in shaping the future of technology.